Getting the most from the orphan drug tax credit requires navigating complex regulations. This guide simplifies the process of using Form 8820 to claim this valuable incentive, focusing on practical application and maximizing your potential savings.
Understanding the Orphan Drug Credit
The orphan drug credit incentivizes pharmaceutical companies to develop treatments for rare diseases (affecting fewer than 200,000 individuals in the U.S., or more than 200,000 but with no reasonable expectation of recouping development costs). It offers a substantial tax break, rewarding investment in treatments for underserved patient populations. However, understanding the nuances of the credit is vital for maximizing its benefits. Are you maximizing your potential savings?
Is Your Drug Eligible? Orphan Drug Qualification
Before completing Form 8820, your drug must meet specific criteria for orphan drug classification. These criteria, detailed in IRS publications, center on the rarity of the targeted disease and the absence of existing, effective treatments. Verifying eligibility upfront is fundamental to a successful claim. Failing to meet these requirements can jeopardize your entire application.
Calculating Your Credit: A Multi-Step Process
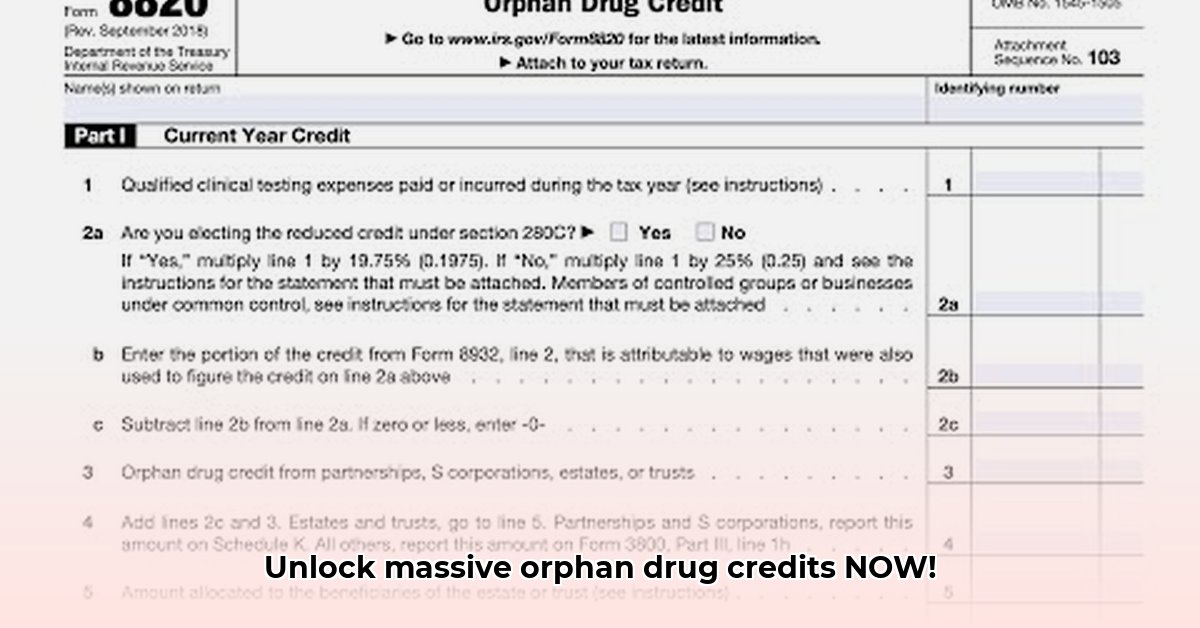
Calculating the orphan drug credit using Form 8820 involves a series of steps. Professional tax guidance is often recommended due to the complexities involved.
1. Identifying Qualified Clinical Testing Expenses
This is the foundation of your calculation. Meticulously document all expenses directly tied to your orphan drug's clinical testing, including salaries, lab fees, and materials. Thorough record-keeping is crucial, as the IRS will require supporting documentation. What percentage of your overall expenses are directly attributable to clinical testing?
2. Determining Qualified Revenue
This refers to the gross revenue (total sales) generated from your orphan drug. This figure is distinct from your profit margin.
3. Applying the Credit Percentage
The credit is a percentage of your qualified clinical testing expenses. This percentage varies based on your qualified revenue, generally increasing as revenue decreases. Consult the latest IRS instructions for the precise percentage brackets. For example, a higher percentage might apply if you achieve lower revenue targets, but what are the limitations?
4. Applying Section 280C Limitations
Section 280C of the Internal Revenue Code restricts the deductibility of certain expenses related to drug creation. It acts as a safeguard, preventing overly generous tax benefits. Understanding this section's limitations is essential for accurate calculation and maximizing your potential credit. This section often presents the greatest challenge. How can you navigate this complexity effectively?
Step-by-Step Guide to Completing Form 8820
The following steps outline the process of completing Form 8820:
Gather Data: Compile comprehensive, organized records of all qualified clinical testing expenses. Thorough documentation is paramount to a successful claim. This step forms the core of your entire application.
Verify Eligibility: Ensure your drug meets all orphan drug classification requirements. Retain documentation proving this eligibility. What are the most commonly overlooked aspects of eligibility verification?
Calculate Credit: Carefully calculate your credit, considering all factors and limitations. Professional assistance is advisable. What are the most frequent errors in the credit calculation?
Complete Form 8820: Fill out the form accurately and completely, double-checking for errors before submission.
File Your Tax Return: Submit the completed Form 8820 with your tax return by the deadline. Missing the deadline could mean forfeiting your credits.
Pros and Cons of Claiming the Orphan Drug Credit
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Substantial tax savings | Complex calculations; professional help often recommended. |
| Encourages R&D for rare disease treatments | Potential limitations via Section 280C; careful planning essential. |
| Competitive advantage in the marketplace | Requires meticulous documentation; detailed records crucial throughout. |
Final Thoughts: Expert Guidance is Key
While the orphan drug credit offers significant tax savings, its complexity necessitates professional tax guidance. The potential benefits are substantial, but inaccuracies can lead to costly consequences. Seeking advice from tax professionals experienced in pharmaceutical tax credits is a prudent investment, safeguarding your claim and ensuring compliance. Remember: accurate, well-documented claims maximize your benefit. "The complexities of Form 8820 and Section 280C necessitate professional expertise to prevent costly errors and maximize the credit’s potential.", says Dr. Eleanor Vance, CPA, Partner at Tax Strategies Group.
"Proper documentation is paramount," adds Michael Chen, Attorney at Law, specializing in pharmaceutical regulations and tax law at Chen & Associates. "This minimizes risk and strengthens your claim during an audit."
Key Takeaways:
- The Orphan Drug Credit, claimed using Form 8820, significantly impacts pharmaceutical company tax liabilities.
- Accurate calculation requires careful attention to qualified expenses and revenue, along with a thorough understanding of Section 280C implications.
- Professional tax advice is essential for navigating the complexities and avoiding potential pitfalls.